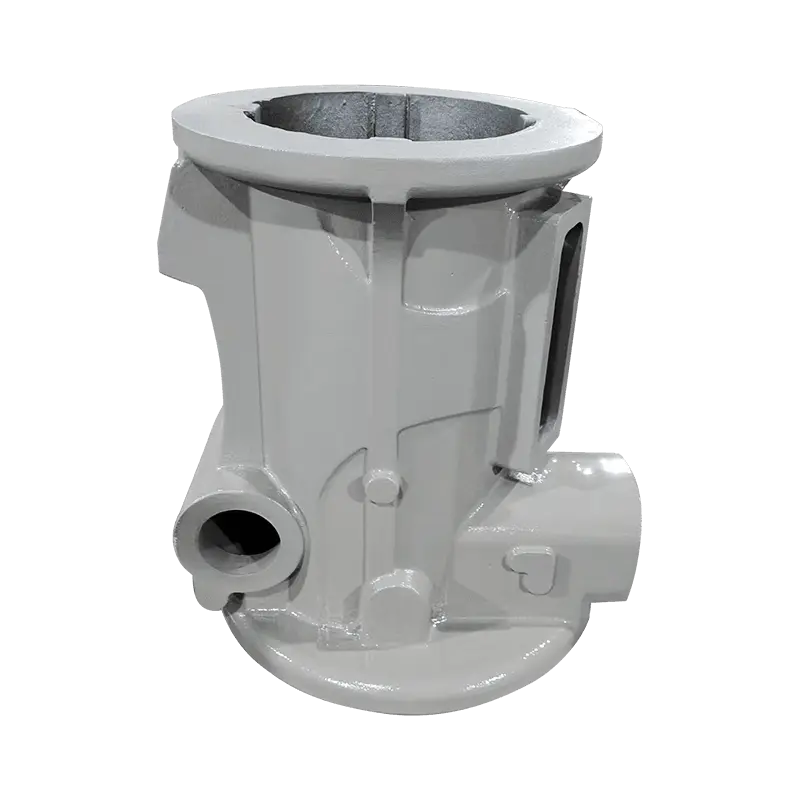
Given that Compressor Coated Sand Cylinders are employed in systems involving high-pressure operations, pressure management is critical to ensure the cylinder remains intact and functions safely. Operating above the cylinder's maximum pressure rating can lead to catastrophic failures, including ruptures or explosions. It is essential for operators to consistently monitor and regulate the pressure levels within the cylinder using pressure gauges and pressure regulators to avoid over-pressurization. The use of pressure relief valves is recommended to provide an automatic means of releasing excess pressure, thereby protecting both the cylinder and the surrounding equipment. These valves should be inspected regularly to ensure they are functioning properly. Operators must also receive training on how to adjust compressor settings to ensure they do not exceed the cylinder’s specified pressure limits, thereby minimizing the risk of damage or failure.
Routine inspection and maintenance are foundational to the longevity and safe operation of Compressor Coated Sand Cylinders. Regularly inspecting the coating integrity is essential, as any chips, cracks, or degradation of the coating could expose the cylinder to external damage or corrosion. Over time, the coated surface may experience wear from abrasive particles in the environment, or from chemical exposure that could compromise its performance. Operators should perform visual inspections for signs of dents, scratches, or rust and should test for any leaks around the cylinder’s valve fittings. Routine maintenance tasks should include cleaning the cylinder to remove any contaminants, inspecting the cylinder’s structural integrity, and performing pressure tests to ensure it can safely handle the required pressure. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule is critical to preventing failure, as it allows for early detection of issues that could lead to costly downtime or hazardous situations.
Compressor Coated Sand Cylinders can be large and heavy, making them challenging to handle without the appropriate equipment. Improper lifting or handling can result in personal injury, damage to the cylinder, or loss of product due to accidents. It is vital for personnel to be trained in safe lifting practices and to use appropriate lifting tools such as hoists, lifting straps, and forklifts. Operators should always wear protective gloves and steel-toed boots to protect themselves from potential injuries from sharp edges or falling cylinders. Cylinders should be moved vertically and stored in a secure, upright position to minimize the risk of toppling. It is also important that handling equipment is inspected regularly to ensure its functionality and that it is capable of safely supporting the cylinder’s weight. Warning labels should be prominently displayed to indicate proper lifting and handling procedures, reducing the chance of accidents caused by improper use.
In environments where Compressor Coated Sand Cylinders are exposed to chemicals or abrasive materials, it is essential to ensure that the cylinder's coating is compatible with the substances being compressed or stored. Certain chemicals or solvents can degrade the protective coating or interact with the steel substrate, which could compromise the integrity of the cylinder. For example, aggressive acids or solvents may cause corrosion or surface deterioration. Operators should review material safety data sheets (MSDS) for any chemicals used with the cylinder and confirm that the cylinder’s coating is designed to withstand such exposures. Preventive measure includes using secondary containment such as spill trays to contain any accidental leaks or spills that might compromise the safety of the equipment. Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respirators should be used when working with hazardous chemicals in proximity to the cylinders.