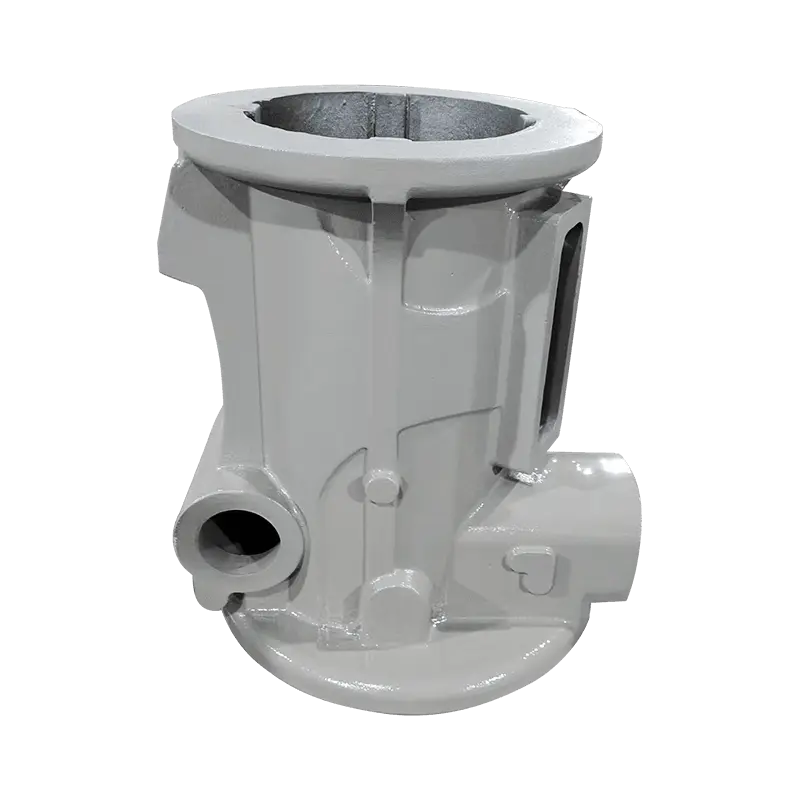
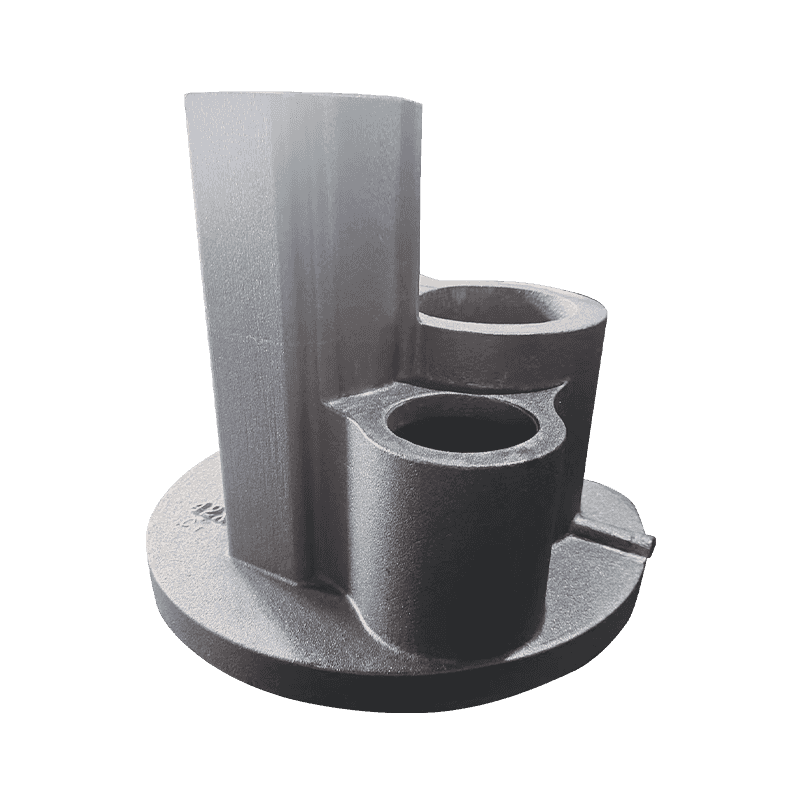
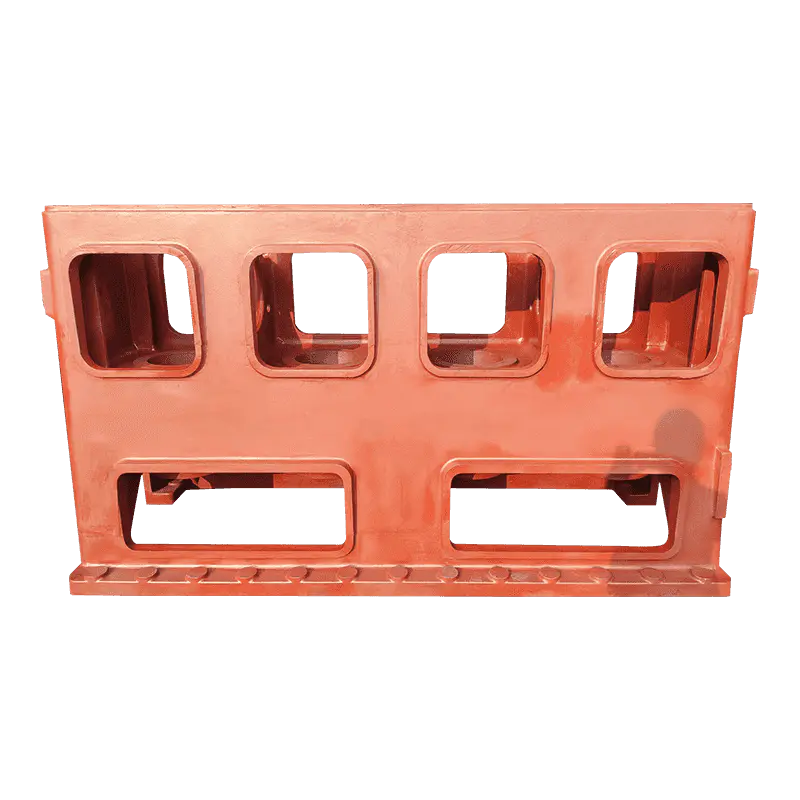
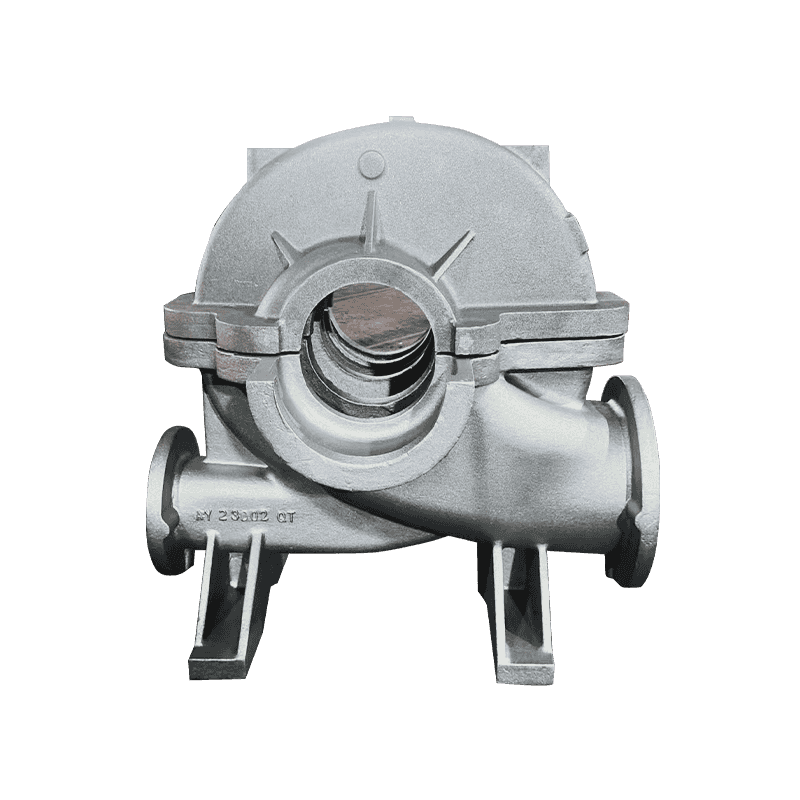
The material selected for Construction Machinery Casting plays a fundamental role in determining the performance and longevity of the component. For example, materials such as high-strength alloy steels, cast iron, or aluminum alloys are chosen based on their specific mechanical properties. Alloy steels are often used in critical load-bearing parts because of their superior tensile strength, while cast iron is used for parts where wear resistance and vibration damping are crucial. On the other hand, aluminum alloys might be selected for their lighter weight without compromising too much on strength. Proper material selection ensures that the casting meets the operational demands of construction machinery, whether in high-stress applications like excavators or under severe weather conditions like those found in outdoor construction environments. This contributes to improved overall machinery reliability and efficiency, as it reduces wear and tear and minimizes the risk of early failure due to material fatigue or environmental stresses.
Achieving high precision and tight tolerances in Construction Machinery Casting is critical to ensure that the components fit seamlessly within the overall assembly of the machinery. High tolerance castings minimize the need for additional machining and adjustments during assembly, which saves time and cost in production while ensuring a higher level of operational efficiency. For example, if a casting has significant dimensional deviations, it can lead to improper fits, causing parts to operate inefficiently, increase friction, or wear out prematurely. Precision in design also ensures that moving parts interact smoothly, preventing unnecessary strain and ensuring the system functions optimally. This tight fitting directly impacts the machinery’s reliability, as properly aligned components reduce the risk of failure and contribute to smoother operation, improving both productivity and safety on the job site.
One of the primary goals in the design of Construction Machinery Casting is optimizing the weight of components without sacrificing their strength or durability. Heavy machinery can significantly impact fuel efficiency and performance, particularly for mobile equipment that needs to move across large construction sites. By using casting methods that incorporate hollow sections, ribbed structures, or lightweight alloys, manufacturers can reduce the weight of components while maintaining their strength and functionality. Optimized weight not only enhances fuel efficiency but also makes the equipment easier to maneuver and reduces the wear and tear on the machine’s transmission and drive systems. However, weight reduction must be carefully balanced with durability to ensure the castings can still handle high loads, vibrations, and external forces without compromising the machinery’s reliability or safety.
Construction machinery is subjected to constant forces, vibrations, and impacts during operation. These conditions create fatigue stresses in components, which can lead to cracks and premature failure if the material is not designed to handle such conditions. Design specifications for Construction Machinery Casting must include provisions for enhancing fatigue resistance, such as reinforcing critical areas that experience the highest stress, optimizing grain structure during casting, or selecting materials with inherent fatigue strength. Components like chassis, axles, or engine mounts often require additional attention to prevent early wear. By accounting for fatigue resistance in the casting design, manufacturers ensure that the machinery operates reliably over a long lifespan, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns and extending the service life of key components.